
Unveiling the Secrets of Energy Efficient Windows
Discover energy-efficient windows: From double glazing to vacuum glazing, learn how to save energy, money, and the environment in your home.
Windows have a bigger role than just connecting rooms. In a time where we care about the environment and saving energy, window efficiency matters. They affect how much energy we use and how comfortable our spaces are. In this journey, we explore how windows work, what makes some better at saving energy, and how they fit into a sustainable lifestyle. Let’s uncover the secrets of window efficiency to make smarter choices for a greener future.
Exploring Window Types and Energy Efficiency
When it comes to energy efficiency in windows, one type that falls short is the single-pane window. These windows, with just one layer of glass, often lack the insulation needed to effectively control indoor temperature. Recognising the energy inefficiency of single-pane windows is an important step in making smarter energy choices. By understanding their limitations, we can make more informed decisions about the windows we choose, leading to improved comfort, lower energy bills, and a more environmentally friendly living space.
The least energy-efficient window type is typically single-pane windows. These windows lack effective thermal barriers, leading to the escape of conditioned air and the ingress of outside air, resulting in energy loss and inefficiency.
What Type of Windows Prevent Heat Loss?
Through this section, we’ll explore the types of windows that effectively prevent heat loss, diving into the technologies and design features that transform windows into proactive insulation barriers. From double glazing to advanced coatings and gas-filled panes, culminating in the revolutionary vacuum glazing, we’ll uncover the arsenal of solutions that redefine the boundaries of energy-efficient living.
Low energy windows, also referred to as Low-E windows, are a transformative innovation in the realm of energy-efficient building design. These windows are equipped with a specialized coating applied to the glass surface, revolutionizing their energy performance. Originally conceived to retain infrared light in colder climates, Low-E windows have evolved into a versatile and cost-efficient option that yields benefits across various regions. By effectively regulating heat transfer, Low-E windows contribute to reduced energy consumption, enhanced indoor comfort, and a greener approach to living.
Deciphering Window Efficiency: A Complex Interaction
The efficiency of windows involves a nuanced interaction of multiple factors, each influencing the overall performance of diverse window types. Window materials, glazing technology, framing, and seal quality are key variables that collectively establish a window’s ability to preserve heat and maintain indoor temperatures.
1. Frame Materials:
- The framing material’s thermal conductivity affects the window’s overall insulation.
- Different materials, such as wood, vinyl, and aluminium, have varying insulating properties.
- Wood, for instance, offers natural insulation, while aluminium conducts heat more readily.
2. Glazing Technology:
- The number of panes and the type of gas filling (argon or krypton) between them impact insulation.
- Low-E (low-emissivity) coatings reduce heat transfer, enhancing efficiency.
3. Seal Quality:
- Airtight seals prevent drafts and heat loss around the window edges.
- Proper seals maintain energy efficiency by preventing air infiltration.
Gaining Insights into these aspects helps us thoroughly assess window choices. By factoring in these elements, we can pick windows that match our energy-saving objectives, fostering increased comfort, reduced utility expenses, and a greener living space.

The Power of Double Glazing
At the core of the double-glazed windows’ heat loss prevention prowess lies the ingeniously designed insulating gap—a space strategically placed between two glass panes. This insulating gap serves as a barrier against heat transfer, curbing the movement of thermal energy between the interior and exterior environments.
While double glazed windows are a popular choice for reducing heat loss due to the insulation created by their air gaps, an even more advanced solution exists in the form of vacuum glazing. Vacuum glazing, exemplified by LandVac Optimum Glazing, takes heat loss prevention to the next level. By utilizing a vacuum-sealed gap between panes, these windows offer unparalleled thermal insulation, elevating energy efficiency and comfort to new heights. The innovation of vacuum glazing represents a breakthrough in the realm of window technology, redefining the possibilities for effective heat loss prevention.
Leveraging Inert Gases for Enhanced Efficiency
Within the intricate framework of double-glazed windows, a quietly influential element resides within the insulating gap – inert gases such as argon or krypton. These gases, chosen for their unique characteristics, play a pivotal role in countering heat conduction – a battle that fundamentally dictates thermal efficiency and energy conservation.
The Role of Denser Gases
Among these gases, argon assumes a remarkable role. Unlike ordinary air, it boasts a higher density that effectively curbs heat conduction. This quality makes argon a powerful barrier against indoor heat loss.
Minimising Heat Transfer
Argon’s sluggish movement is another asset. Its slow convection rate means less heat transfer, which ultimately translates to minimised heat loss. This deliberate movement restrains heat from escaping through the window, contributing to improved thermal performance.
Elevating Thermal Efficiency
In simple terms, argon’s thickness and slow movement work together to stop heat from spreading. This makes double-glazed windows with argon a strong shield against energy loss. It keeps indoor spaces cozy and helps save energy in a sustainable way.
Low-E Coatings for Optimal Insulation
In the realm of cutting-edge window technology, a game-changer emerges in the form of Low-E (low-emissivity) coatings. These seemingly unassuming coatings wield the power to transform windows into veritable energy conservation champions, making them a formidable force in the quest to prevent heat loss and elevate thermal performance.
Unleashing the Power of Low-E Coatings
Low-E coatings are carefully engineered layers that serve as a thermal barrier on glass surfaces. These coatings are designed to exhibit a remarkable property: they are highly reflective to infrared radiation. This unique attribute forms the foundation for their pivotal role in heat loss prevention.
Reflecting Heat Back into the Room
The magic of Low-E coatings lies in their ability to reflect radiant heat back into the room from which it originates. When interior heat attempts to escape through the window, the coatings act as a mirror, redirecting the heat back indoors. This prevents valuable warmth from dissipating into the cold outdoors.
Preserving the Influx of Natural Light
While Low-E coatings excel at reflecting heat, they do not compromise on another crucial aspect: natural light. These coatings are strategically engineered to allow visible light to pass through unimpeded. This means that while heat is redirected, the influx of beautiful natural light remains unhindered, contributing to a well-lit and inviting living space.
Low-Emissivity (Low-E) coatings function by being applied to glazing units, aiming to minimise the absorption and subsequent emission of heat from the glazing to the external environment. Through this application, Low-E coatings effectively reflect radiant heat back into the internal spaces, resulting in enhanced thermal performance of the glass unit.
Amidst the realm of window innovation, Low-E coatings shine as beacons that skillfully manage the interplay of heat reflection and light transmission. Their adeptness in redirecting heat while allowing natural light to pass through makes them stalwart protectors of comfort and energy efficiency.
The Vanguard of Efficiency: Vacuum Glazing
Amidst the ongoing strides in the window industry towards energy conservation, vacuum glazing emerges as a pioneering force in preventing heat loss. This ingenious advancement goes beyond traditional methods, utilizing a vacuum-sealed gap between panes to establish an unparalleled shield against the transfer of thermal energy. In this segment, we delve into the captivating domain of vacuum glazing, revealing its complexities, attributes, and the extraordinary potential it bears for fostering energy-efficient lifestyles.
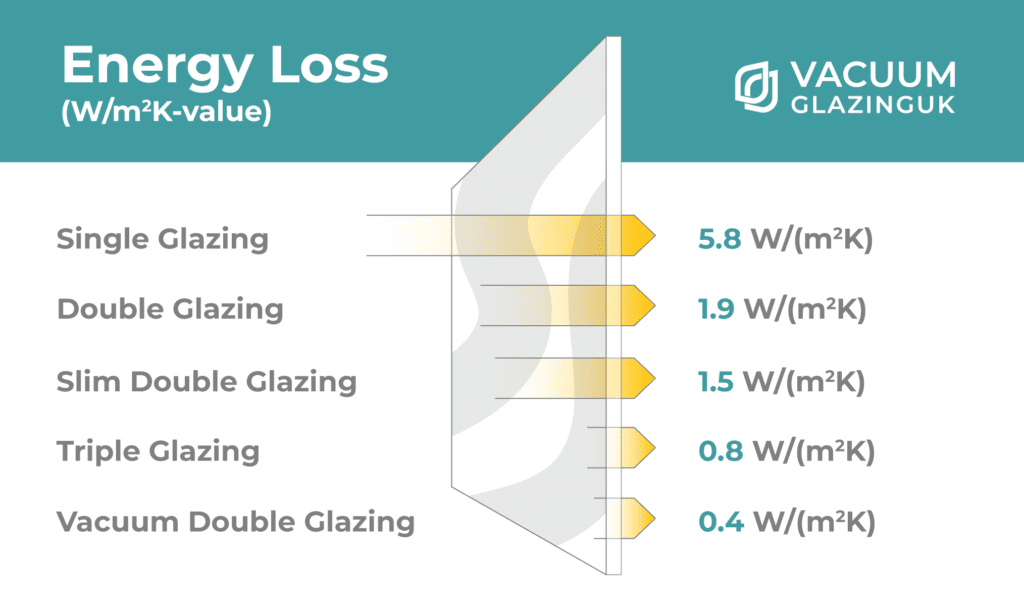
Harnessing the Power of a Vacuum Gap
At the core of vacuum glazing lies a concept that defies tradition—the introduction of a vacuum-sealed gap between panes. This vacuum acts as an insurmountable obstacle to heat transfer, drastically reducing the movement of thermal energy. By creating a vacuum environment, these windows redefine the standards of insulation and reconfigure the energy dynamics of living spaces.
Vacuum insulation is the best insulator because it lacks atoms, stopping heat transfer effectively. Lacking atoms in a vacuum stops heat transfer because heat is primarily conducted through atomic collisions and carried by atoms. In a vacuum, there are no atoms to carry heat through conduction or convection, making it an efficient insulator. Without atoms to transfer heat energy, the movement of thermal energy is greatly restricted, resulting in minimal heat transfer.
Triple Glazing and Beyond
Vacuum glazing is a combination of different layers, each playing a role in its outstanding performance. These windows are carefully designed with triple glazing, special coatings, and argon gas fills to be incredibly energy-efficient. Unlike regular slim double glazing, which can sometimes be less stable, vacuum glazing is known for its reliability and consistent performance over the years.
LandVac Optimum Glazing
In the world of vacuum glazing, LandVac Optimum Glazing stands out for its excellence. LandVac aims to break limits and offers industry-leading low U-values of 0.4, which means exceptional energy savings. These windows blend innovation and reliability, assuring long-lasting efficiency and a more environmentally friendly impact.
Choosing the Right Window for Energy Efficiency
Having delved into the details of energy efficient windows, we’ve gathered valuable insights for an energy-conscious lifestyle. In this part, we simplify the lessons learned and provide practical advice for homeowners aiming to find the best energy-efficient windows. As we make informed choices, we realise that picking the right windows involves various factors beyond just the type, forming a comprehensive approach to energy efficiency.

Several factors can influence a buyer’s choice of windows:
1. Energy Efficiency:
Buyers often prioritise windows that contribute to energy savings by preventing heat loss and reducing the need for heating and cooling systems.
Choose:
- Double-glazed or triple-glazed windows with low-E coatings and gas fills (argon or krypton) for enhanced insulation.
- Vacuum-glazed windows for superior thermal performance.
- Consider sash windows with slim double glazing for a combination of aesthetics and efficiency.
2. Aesthetics
The visual appeal of windows and how well they complement the architectural style of a building can significantly impact a buyer’s decision.
Choose:
- Sash windows for a classic and timeless look.
- Casement windows for a more contemporary appearance.
- Customisable frames and mullions to match architectural styles.
3. Functionality
Buyers consider factors like ease of operation, ventilation options, and the ability to regulate light and privacy.
Choose:
- Casement windows for easy operation and excellent ventilation.
- Tilt and turn windows for versatile opening options.
- Top-hung windows for maximum airflow without obstructing views.
4. Durability
Windows that are made from high-quality materials and designed to withstand various weather conditions are more attractive to buyers.
Choose:
- Timber framesm made from Accoya® for long-lasting durability.
- Tempered or laminated glass for added strength and safety.
- Avoid Slim Double glazing as it has reliability issues
5. Maintenance
Low-maintenance windows are favoured, as they reduce the need for frequent cleaning and repairs.
Choose:
- UPVC frames require minimal maintenance and are easy to clean.
- Timber frames from Accoya® have an exceptional service life
- Self-cleaning glass coatings that reduce the need for regular cleaning.
6. Noise Reduction
Windows with sound insulation properties are appealing, especially for properties located in noisy areas.
Choose:
- Double-glazed windows with laminated glass for sound insulation.
- Vacuum-glazed windows for exceptional noise reduction.
7. Security
Buyers look for windows that provide enhanced security features, helping them feel safe and protected.
Choose:
- Multi-point locking systems for enhanced security.
- Laminated glass that remains intact even when shattered.
- Toughened or tempered glass
8. Cost
The initial cost of energy efficient windows and potential long-term savings in energy bills are important factors in the decision-making process.
Choose:
- UPVC frames for a cost-effective option.
- Double-glazed windows with standard low-E coatings for a balance between cost and energy efficiency.
- More expensive options can offer better long term savings as they have longer service lives, require less maintenance and are more efficient.
9. Environmental Impact
Eco-conscious buyers may prioritise windows made from sustainable materials that have minimal environmental impact.
Choose:
- Timber frames from sustainably sourced wood.
- Low-E coatings and vacuum glazing for reduced energy consumption.
10. Local Climate
Climate considerations influence choices, such as opting for windows that provide good insulation in colder climates or that block excessive heat in warmer climates.
Choose:
- Double-glazed windows for either warmer or colder climates.
- Tinted or reflective coatings to block excessive heat in warmer climates.
11. Regulations and Standards
Compliance with building codes, energy efficiency standards, and historical preservation regulations may play a role in window selection.
Choose:
- Historic homes: windows with heritage glazing and materials to comply with preservation requirements.
- Energy efficiency standards: Windows that pass Parts L and Q of Building regulations, e.g. LandVac Optimum
12. Resale Value
Buyers often consider how window choices might impact the resale value of a property.
Choose:
- High-quality materials and advanced glazing options that enhance energy efficiency and aesthetics.
- See this post on Do Sash Windows add Value to Property?
Considering these factors allows buyers to make informed decisions that align with their preferences, needs, and values.
Conclusion: Embracing Energy-Efficient Living Through Smart Window Choices
Our exploration of window efficiency has uncovered valuable insights for a more environmentally friendly way of life. Windows, often seen as simple openings, hold immense importance in today’s world where saving energy matters.
We’ve learned that single-pane windows waste energy because they lack proper insulation. On the flip side, double glazing and vacuum glazing are game-changers. They create layers of protection against heat loss, making our homes more comfortable and efficient.
We also looked at important things to consider when choosing windows. We talked about energy efficiency, which means picking windows that save energy and money. We discussed how windows look, how they work, how durable they are, and their impact on the environment. We even considered factors like the climate where we live and the rules we need to follow.
Our journey to energy efficiency is a journey towards a brighter, greener future. By making informed choices about windows, we’re not only making our homes better but also taking care of our planet. Let’s remember that every small choice counts in creating a more sustainable world for us and the generations to come.